GitHub: How To Enable Code Scanning With Semgrep
Semgrep is an incredible static analysis engine that can be used for finding bugs, detecting vulnerabilities and even for enforcing code standards. Semgrep is a Swiss army knife for static code analysis.
This article describes how to automate the discovery of coding vulnerabilities with Semgrep and GitHub Workflows. For this, we will need 2 workflows: full scan and differential scan.
Full scan
The first workflow is dedicated to scan all the codebase of your application and provides a global analysis of the existing.
To create this workflow, paste the following content in .github/workflows/semgrep-full.yaml:
---
name: Semgrep Full Scan
on:
workflow_dispatch:
branches:
- main
schedule:
- cron: '0 1 * * 6'
jobs:
semgrep-full:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
container:
image: returntocorp/semgrep
steps:
# step 1
- name: clone application source code
uses: actions/checkout@v3
# step 2
- name: full scan
run: |
semgrep \
--sarif --output report.sarif \
--metrics=off \
--config="p/default"
# step 3
- name: save report as pipeline artifact
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v3
with:
name: report.sarif
path: report.sarif
# step 4
- name: publish code scanning alerts
uses: github/codeql-action/upload-sarif@v2
with:
sarif_file: report.sarif
category: semgrep
Then, you can manually trigger this workflow to run a first full scan.
All findings will be published in the Code Scanning alerts in the Security tab of your GitHub repository.
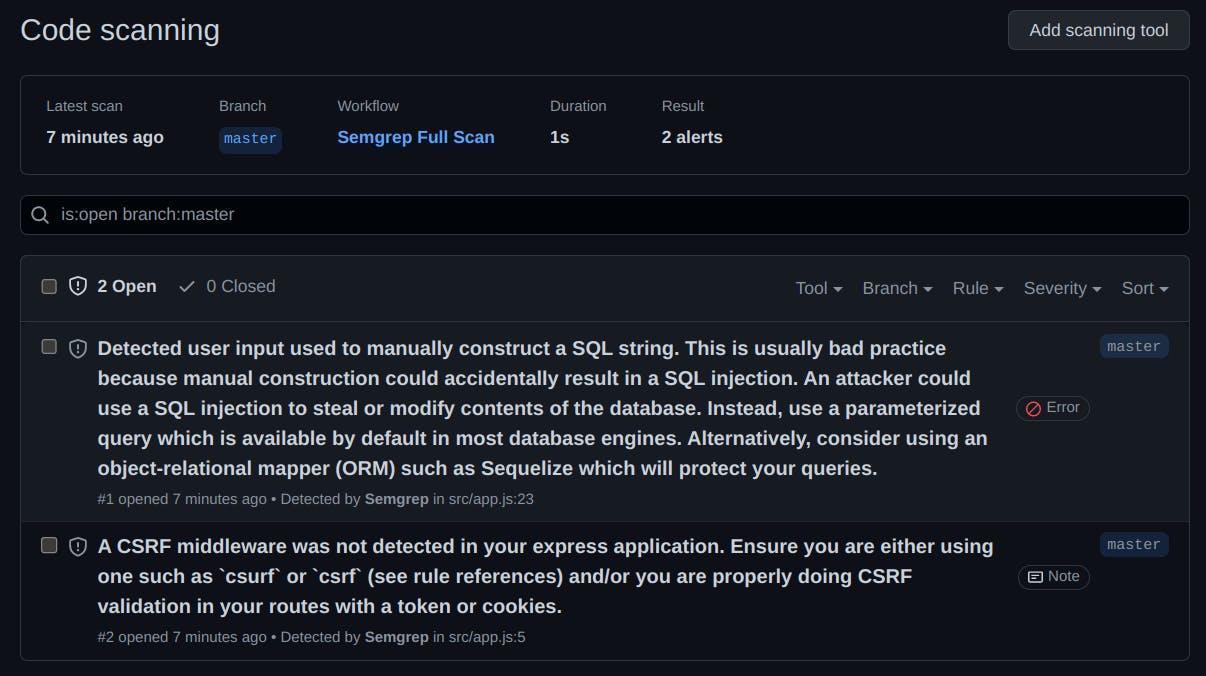
This workflow is also scheduled to run a full scan every Saturday at 1:00 AM.
And the result is sync with the Code Scanning Alerts dashboard.
New findings are published and fixed findings are automatically closed.
This is an immensely cool feature!
Code Scanning alertsis free for public repositories but organisations must subscribe toGitHub Advanced Securitywhich is a very expensive add-on. If you don't have this option, and you don’t want to subscribe, you can use another security dashboard like Defect Dojo.
... and it’s that simple. The first workflow is now operational!
Now, you’ll probably discover that you have a lot of findings in your Code Scanning Alerts dashboard.
We know that it will not be possible to fix all of them immediately.
Fixing those will probably need several weeks of work.
That is why this workflow can't block the software pipeline.
However, thanks to this workflow, you can follow your progress because, each week, fixed alerts are automatically closed.
While waiting for these corrections, you can block all Pull Requests which could add new findings. For that, we can write a second workflow to run a differential scan in order to report only findings in the Pull Requests.
Differential scan
The second workflow is dedicated to analyse Pull Requests.
To create this workflow, paste the following content in .github/workflows/semgrep-diff.yaml:
---
name: Semgrep Differential Scan
on:
pull_request
jobs:
semgrep-diff:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
container:
image: returntocorp/semgrep
steps:
# step 1
- name: clone application source code
uses: actions/checkout@v3
with:
fetch-depth: 0
# step 2
- name: differential scan
run: |
semgrep scan \
--error \
--metrics=off \
--baseline-commit ${{ github.event.pull_request.base.sha }} \
--config="p/default"
Under the hood, Semgrep performs two scans: one on the Pull Request and another on the existing codebase before the Pull Request. Therefore, only new findings are reported.
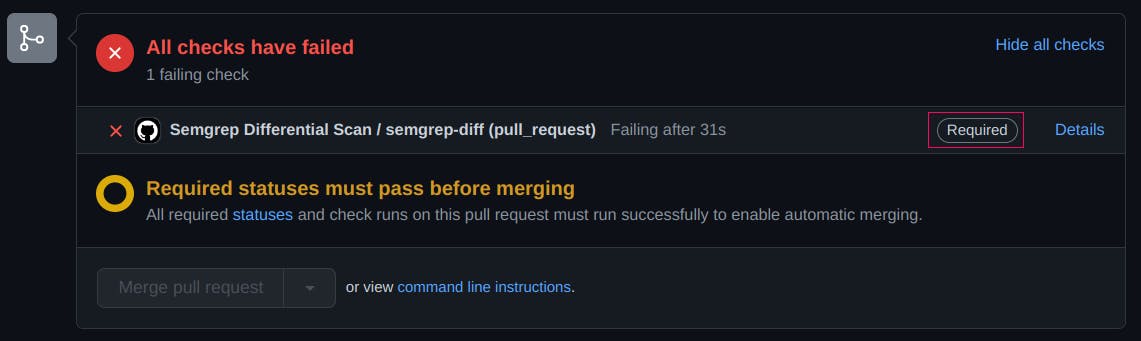
Now, you can protect your default branch main in your repository settings, by adding semgrep-diff in Require status checks to pass before merging.
By the way, you can also check Do not allow bypassing the above settings to prevent Semgrep bypass.
After that, it will not be possible to merge thes Pull Requests with new findings:
Wrap-Up
Congratulations! You have setup Semgrep on your GitHub repository with two workflows:
- A workflow to perform a full scan on the existing codebase
- A workflow to perform a differential scan on Pull Request
Using Semgrep with GitHub this way provides more flexibility. As you can see, you can enable code scanning without having to fix all of the findings on your existing codebase.
Take the time to assess the risks of each finding in order to prioritise them. In the meantime, you will be sure that there will be no additional findings in your repository, and you can even change the rules without freezing any developments.